Ferocactus latispinus Care, Propagation and Tips Guide (2023)
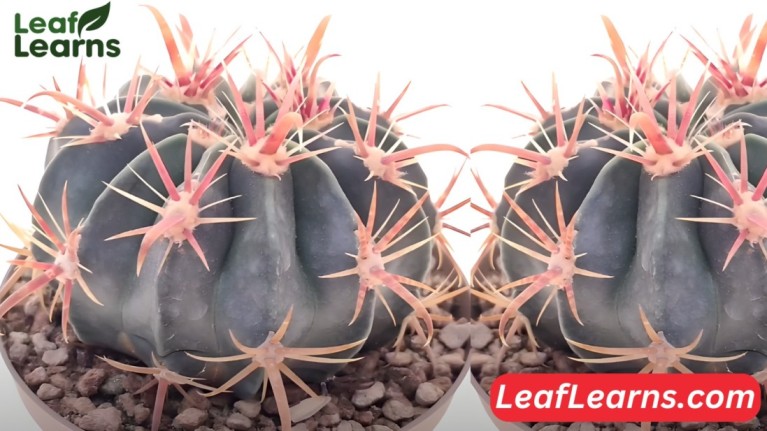
Devil’s Tongue Barrel or Candy Cactus known commonly as Ferocactus latispinus, lives in arid regions of Mexico and is a fascinating species of barrel cactus. It has captivated cactus enthusiasts worldwide due to its distinct spines and vibrant blooms.

Contents
- 1 Overview of Ferocactus-latispinus
- 2 Understanding its Unique Features
- 3 Top Care Tips
- 4 What is Ferocactus-latispinus?
- 5 Origins and Distribution
- 6 Care for Ferocactus latispinus
- 7 Watering Practices
- 8 Temperature Needs
- 9 Air Humidity Considerations
- 10 Soil Preferences
- 11 Fertilizing Requirements and Tips
- 12 Physical Characteristics
- 13 Propagation and Growth
- 14 How to Repotting
- 15 Pruning Guidelines
- 16 Common Problems and Solutions
- 17 Pest Management
- 18 Addressing Growing Issues
- 19 Toxicity of Ferocactus-latispinus
- 20 Suggested Uses
- 21 Top Tips for Optimal Growth
- 22 Exploring the Market
- 23 Varieties and Types
- 24 Comprehensive Care Guide for Ferocactus latispinus and Diverse Cactus Varieties
- 25 Conclusion
- 26 FAQs
Overview of Ferocactus-latispinus
Ferocactus latispinus is commonly found as a solitary globular specimen. It features 21 acute ribs adorned with impressive spines on its stem, which ranges from light green to blue-green.
As a formidable defense against predators, the spines are flattened and range from a reddish to white color.
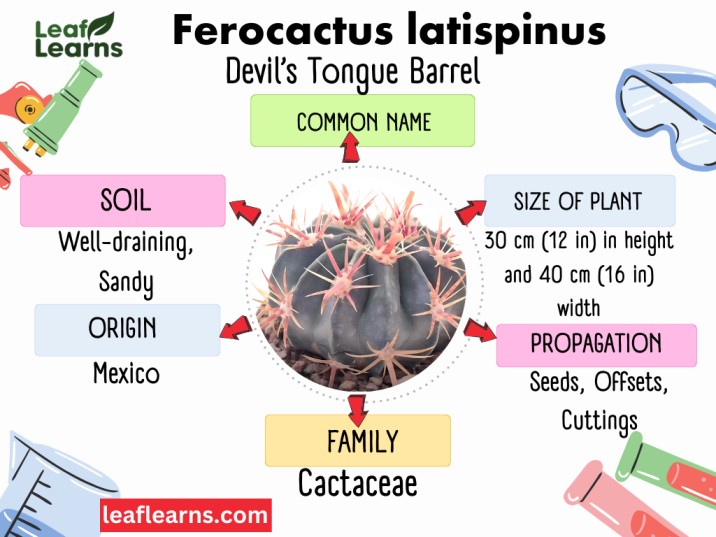
| Common Name | Candy cactus, Devil’s Tongue Barrel, Crow’s Claw Cactus |
| Scientific Name | Ferocactus-latispinus |
| Family | Cactaceae |
| Origin | Mexico |
| Plant Type | Succulent Cactus |
| Size | 30 cm (12 in) in height and 40 cm (16 in) width |
| Leaf Color | N/A (Succulent with spines) |
| Leaf Size | N/A (Spines instead of leaves) |
| Flower | Yellow to Red |
| Light | Full Sun |
| Water | Low to Moderate |
| Soil | Well-draining, Sandy |
| Temperature | 50°F to 100°F (10°C to 38°C) |
| Humidity | Low |
| Fertilizer | Cactus or Succulent Fertilizer |
| Propagation | Seeds, Offsets, Cuttings |
| Pruning | Minimal |
| Pests | Spider Mites, Aphids, Scale |
| Toxicity | Mildly Toxic to Humans and Pets |
| Uses | Ornamental, Xeriscaping, Gardens |
Understanding its Unique Features
A remarkable adaptation to harsh environments sets Devil’s Tongue Barrel apart from its fellow cacti. When the soil is parched, its deep roots efficiently extract water from the parched surface, retaining moisture during dry periods.
Top Care Tips
Summer: Ferocactus-latispinus thrives in the harsh summer sun with little water. For overheating to be prevented, adequate air circulation is important.
A dormant phase of this plant occurs during winter as freezing temperatures set in. To prevent root rot, you need a potting mix that drains well.
The Ferocactus plant begins its growth cycle again with the arrival of spring and fall temperatures. In order to support its revitalization, it needs regular watering and increased sunlight.
What is Ferocactus-latispinus?
This mesmerizing species of barrel cactus is a native of Mexico’s arid regions and also known as the Devil’s Tongue Barrel or Candy Cactus. Its distinctive spines and vibrant blooms make it one of the most popular plants.
Origins and Distribution
There are several different forms of this species, but it is most commonly found in the dry, rocky hills and plains of central Mexico, mostly in the states of Guanajuato, Hidalgo, Querétaro, San Luis Potosí, and Tamaulipas. A typical elevation range for it is 1,000 to 1,800 meters above sea level.
Water conservation and survival are key characteristics of this species, which are well-adapted to its arid habitat. Water is efficiently extracted from parched soil by its deep root system with its thick, waxy skin.
Care for Ferocactus latispinus

Light Requirement
Its spring and fall growth cycles are energized by a gentle dose of sunlight to ensure it remains active.
Summer: Let your Ferocactus plant bask in the warmth of summer by exposing it to plenty of sunlight. For your cactus to remain comfortable in its sun-drenched paradise, it is crucial that there is adequate air circulation.
Winter: Make sure your Devil’s Tongue Barrel receives a few hours of gentle sunlight each day as temperatures drop, to maintain its dormancy and prepare for spring.
Spring and Fall: During warmer months, gradually increase the amount of sunlight your Ferocactus-latispinus is exposed to, to allow it to adapt to the increased light intensity. Its revitalization and growth will be supported by regular watering as a result of the increased sunlight.
Watering Practices
It is important to water your this plant infrequently during the hot, dry summer months. Overwatering can lead to root rot, so let the soil dry completely between waterings.
The plant should be watered significantly less during the winter as temperatures drop and it enters dormancy. Make sure the soil feels completely dry before watering the cactus.
Fall and spring: Ferocactus-latispinus grows actively with the return of warmer weather. In order to prevent waterlogging, gradually increase the frequency of watering.
Additional Watering Tips
- The water you use for watering should be at room temperature.
- The excess water should be drained completely after you have watered deeply and thoroughly.
- Cactus bodies should not be exposed to water, as this could cause rot.
- If the stems or bulges on the cactus show signs of swelling, then it has been overwatered.
Temperature Needs
Towards the warm end of the temperature range, It prefers temperatures of 20°C to 35°C. A few degrees of frost (32°F) is tolerable for a short period of time, but prolonged exposure to cold temperatures can damage the plant.
Summer: This plant can thrives in full sun and warm temperatures during the summer months. Overheating can be prevented by providing ample air circulation.
Let the soil dry completely between waterings, watering the cactus deeply but infrequently.
Winter: With the approaching of winter, Devil’s Tongue Barrel enters a dormant state. Water the plant less and place it in an area with bright indirect light. Cactus should not be exposed to frost.
Spring and Fall: As warm weather returns, Ferocactus-latispinus resumes its growth cycle. The amount of water and sunlight should be gradually increased.
Air Humidity Considerations
The optimal development and well-being of plants depends on understanding their seasonal humidity preferences.
This plant thrives in low humidity conditions during the hot and dry summer months. It is best to avoid misting the cactus or placing it next to a humidifier because excessive humidity can cause fungal diseases.
Ferocactus-latispinus enters a dormant state as winter approaches, necessitating even lower humidity levels.
To prevent moisture buildup and potential rot, it is crucial to maintain a dry environment around the cactus during this period.
Devil’s Tongue Barrel resums its active growth cycle in the spring and fall when temperatures warm up and the number of hours of sunlight increases.
In these seasons, misting or placing the cactus near a humidifier for short periods will provide it with a boost of moisture.
Soil Preferences
Despite its resilience, Ferocactus-latispinus prefers soil that drains well and contains fine sand. Cacti often suffer from root rot due to this type of soil, which allows excess water to quickly escape.
Water and sunlight are essential to Devil’s Tongue Barrel in summer. The soil should be allowed to dry completely between waterings, however.
As Ferocactus plant grows in winter, it will require less water, and frost protection is essential. Frost blankets or bringing it indoors can be used to do this.
Water and sunlight are essential in spring and fall for this plant. The cactus can be fertilized with a cactus fertilizer once a month during these seasons.
It can prefers soils that are slightly acidic to neutral, with a pH range between 6.0 and 7.0.
Soil Mix: A good soil mix for Ferocactus-latispinus is:
- 2 parts perlite
- 1 part potting soil
- 1 part sand
You can also add a small amount of compost or eggshell powder to the soil mix to increase fertility.
Fertilizing Requirements and Tips

Fertilizing Ferocactus-latispinus, a cactus that thrives on little fertilizer, is not necessary to ensure its success.
To meet its nutritional requirements, a diluted liquid fertilizer applied once a month is sufficient during its active growth periods in spring, summer, and fall.
It is important to use moderation when fertilizing the plant, because overfertilizing can damage it.
During the winter months when plants go into dormancy, fertilization is not needed. In order to conserve its energy for the growing season ahead, the cactus is allowed to rest without being fed with nutrients.
Fertilizing Tips
- Fertilize sparingly. Fertilizer is not necessary for this plant because it is a desert plant. Plants can be damaged by overfertilization.
- Use a balanced fertilizer. In order to get the best results from Devil’s Tongue Barrel, it is recommended that you use a fertilizer with a 20-20-20 ratio.
- Fertilize during the active growing season. Spring and summer are the active growing seasons.
- Dilute the fertilizer. The fertilizer should be diluted half strength before it is applied to the plant.
- Water the plant after fertilizing. The fertilizer will soak into the soil better if the plant is watered after fertilizing.
Physical Characteristics
The Devil’s Tongue Barrel is a stout, globular-stemmed barrel-shaped cactus with a barrel-shaped flower. It is also known as the Candy Cactus. Among its fellow cacti, it stands out due to its distinctive physical characteristics.
Size and Growth Rate
In general, this fascinating cactus measures 30 centimeters (12 inches) in height and 40 centimeters (16 inches) in width.
There are, however, exceptional specimens that grow as high as 60 centimeters (24 inches), adding an element of grandeur to the desert landscape.
As a result of its slow, but steady growth rate, It can grows about 2.5 centimeters (1 inch) per year. To reach full maturity, Ferocactus-latispinus typically takes around 10 years.
Flowering and Foliage
Devil’s Tongue Barrel bursting with blooms during the spring and summer adds color to an otherwise arid landscape.

Flowers of this plant emit a pleasant scent that attracts pollinators. They range in color from rich rose to purple or straw-yellow.
Cactus foliage has stout spines that, in the harsh desert environment, help conserve moisture and protect the plant from predators.
Unique Features
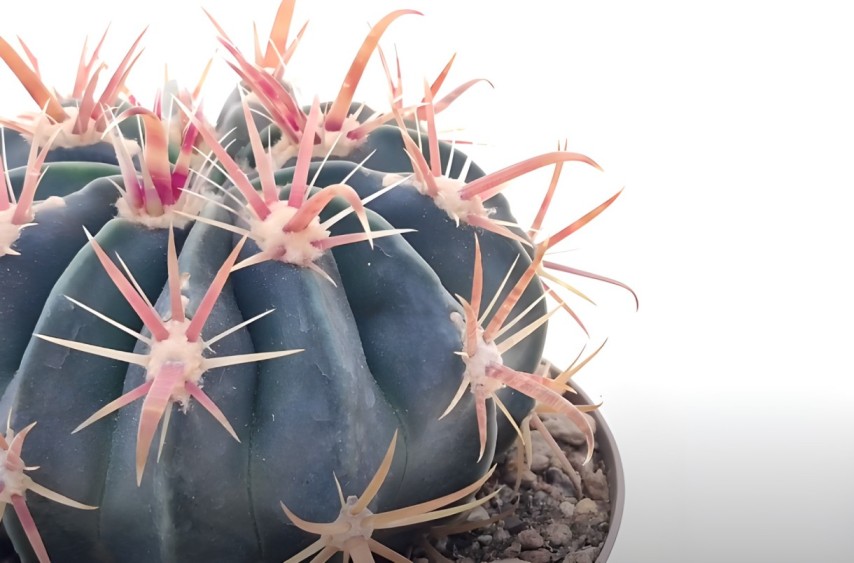
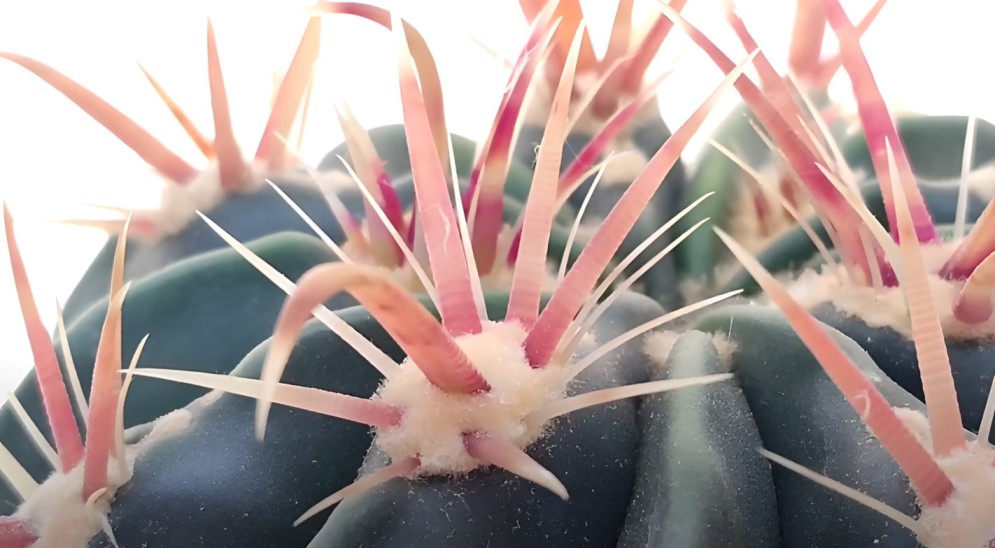
The spines of Ferocactus plant can reach a length of up to 5 centimeters (2 inches), ranging from reddish to white in color.
In combination, these flattened and clustered spines create an effective defense mechanism, protecting the cactus from potential danger.
The cactus’ thick, waxy skin enhances its ability to survive in arid environments, as well as its deep root system that extracts water from the parched soil efficiently.
The flowers of this plant are another unique feature. Typically purple in color, these flowers have a funnel shape and are large. Color is added to the cactus’ otherwise green exterior when they bloom in spring and summer.
Aroma and Fragrance
The aroma and fragrance of Devil’s Tongue Barrel are not strong. There have however been reports that the flowers smell faintly sweet.
Propagation and Growth
Offsetting
In most cases, Ferocactus-latispinus can be multiplied by offset propagation. During its maturity, cacti produce tiny, offset-like growths around their base, known as offsets.
Offsets such as these are ready to live independently, as they have their own root systems.
Steps to Successful Offsetting
- The Right Time to Separate: Try to separate offsets after they’ve grown to a considerable size, usually around 3-4 inches in diameter.
- The offset should be gently separated from the mother plant with a sharp, sterilized knife or pruning shears. The main body or roots of the cactus should not be damaged.
- It is best to callous over the cut end of the offset overnight prior to planting it in a cactus potting mix that drains well.
- The freshly potted offset should be placed in a bright, indirect location with good light. Plants should be watered sparingly until they become established.
Stem Cuttings
You can multiply this plant by stem cutting propagation. In this technique, cuttings are taken from healthy stems on the parent plant and encouraged to root.
Steps to Successful Stem Cutting Propagation
- It is important to select a healthy, mature stem section whose length is between 4-6 inches.
- Making a clean cut at the base of the stem section with a sharp, sterilized knife is the first step in preparation. After the cut has been made, allow it to callous over for a few days.
- The calloused stem cutting should be planted and cared for in a cactus potting mix that drains well and is partially buried before planting. Ensure that the plant receives indirect light and water sparingly.
- In order to develop roots in stem cuttings, you must be patient with them. It may take several weeks or even months. It takes time for new growth to appear, so be patient and provide consistent care.
Seed Sowing
In contrast to stem cuttings and offsettings, seed sowing provides the satisfaction of nurturing a Ferocactus-latispinus from seed to full maturity.
Steps to Successful Seed Sowing
- Ensure the seeds are dry and mature before collecting them from ripe Devil’s Tongue Barrel fruits.
- Sow cactus seeds in a well-draining potting mix that has been sterilized to prevent fungal growth.
- A thin layer of sand or grit should be sprinkled over the potting mix surface before sowing the seeds. Moisture should be provided to the soil, but it should not be too wet.
- Patience and warmth: Place the seed tray in an indirect light location that is warm and humid. There can be a long time between germination and emergence.
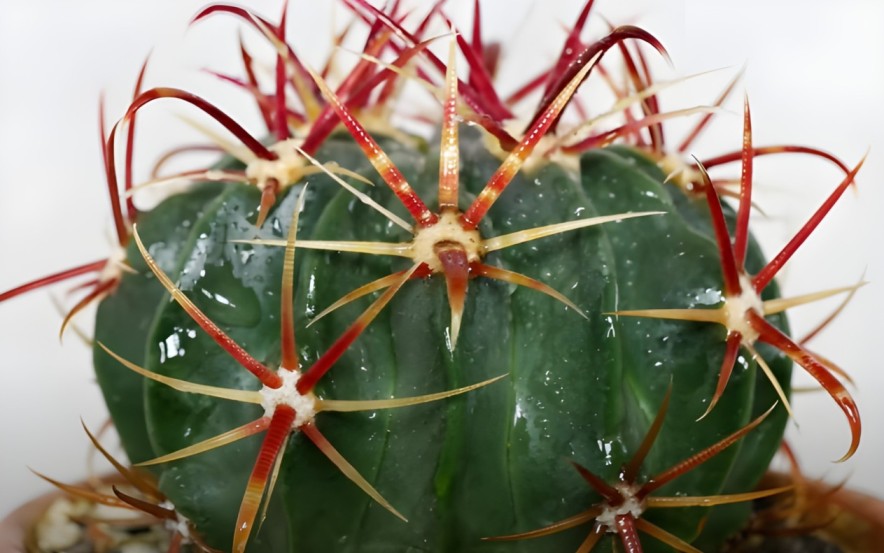

How to Repotting
When to Repot
When Ferocactus-latispinus is actively growing, it is best to repot it during spring and summer. The cactus may need to be repotted more frequently if it is young and growing fast. Repotted cactus show the following signs:
- Drainage holes in the pot have roots growing out of them
- Too small of a pot causes the cactus to topple over
- Cactus growth has stopped or new growth is not being produced
How to Repot
- You should choose a larger pot than the one you currently have.
- For succulents and cacti, use a potting mix that drains well.
- From the pot that the cactus is currently in, gently remove it.
- Make sure that the cactus’ base is at the same level as it was in the old pot before placing it in the new pot and filling it with potting mix.
- Once the drainage holes have been filled, thoroughly water the cactus.
Pruning Guidelines
When to Prune
- The plant must be removed immediately if any part is damaged or diseased, so as to prevent disease spread.
- Overcrowding can be prevented by removing some offsets if a plant produces too many.
- It is possible to remove some of the spines or ribs of the plant in order to shape it into a particular shape.
How to Prune
- Make sure your tools are sharp and sterilized to help prevent disease transmission.
- Ensure that the plant tissue is not torn or bruised when cutting.
- It is important to allow a cut to callus over before treating it with antibiotics.
Common Problems and Solutions
Like all plants, Ferocactus plant is susceptible to certain problems that can affect its health and growth.
Overwatering
Overwatering is a common problem with this type of plants. This can cause root rot, which is a deadly disease. During the dry period between waterings, it is important not to overwater the soil.
Solution
- Cactus cactus prefers to be watered less often in the winter when it is dormant.
- Water should not be trapped in the soil by using a well-draining potting mix.
- Insert a finger into the pot before watering to check the soil moisture level. It is a good idea to wait a few days before watering the soil if it feels moist.
Root Rot
It has been mentioned previously that Ferocactus-latispinus is susceptible to root rot. Symptoms of fungus infection include a plant’s roots being unable to absorb water and nutrients, leading to death.
Solution
- Ferocactus-latispinus may have root rot if it’s been left in its pot for too long. Take it out of its pot and inspect its roots. In the event of brown or mushy roots, or if they smell foul, they should be removed.
- Using a sharp, sterile knife, remove any diseased roots.
- The cactus needs to be replanted in fresh potting soil that drains well.
- In between waterings, be sure the cactus is completely dry.
Pest Infestation
Insects such as mealybugs and scale larvae can also infest Devil’s Tongue Barrel. The sap from the cactus can be sucked away by these pests, which can weaken the plant.
Solution
- Keep an eye out for signs of pests in your Ferocactus plant.
- An alcohol-soaked cotton swab can be used to remove pests if you see them.
- Insecticide soaps and sprays are also available in the market to control pests.
Sunburn
A sun-loving cactus, Devil’s Tongue Barrels can still get sunburned if exposed to too much direct sunlight, especially after spending extended periods of time indoors.
Solution
- During the first few weeks of growing, gradually expose your Ferocactus-latispinus to more sunlight.
- You should provide some shade for your cactus during the hotter parts of the day.
Cold Damage
Frost-hardiness is not a feature of Ferocactus-latispinus, so it should be protected from cold temperatures.
Solution
- This plant should be brought indoors during the winter if you live in a cold climate.
- Use a mulch or frost blanket to protect your cactus from the cold if you can’t bring it indoors.
Pest Management
- Mealybugs: These small, white insects consume your cactus’ sap, leaving a cottony residue behind.
- Scale insects: Cactus are attacked by these armored pests, which suck out the plant’s juices.
- Spider mites: Adopting a webbed structure on leaves, these tiny arachnids cause discoloration and damage to your cactus.
Treatment Options
- Mealybugs: You can remove mealybugs with rubbing alcohol. It may be necessary to use insecticidal soap for larger infestations.
- Scale insects: You can smother scale insects with vegetable oil. It may be effective to apply neem oil to stubborn infestations.
- Spider mites: Neem oil or insecticidal soap are effective at controlling spider mites.
Disease Prevention
- Overwatering: Cactus can suffer from root rot if they are overwatered. Between waterings, let the soil completely dry out.
- Poor drainage: Drainage holes are necessary to keep your cactus pot dry.
- Humid conditions: Ferocactus-latispinus prefers dry weather. It should not be placed in humid environments or over-mistered.

Addressing Growing Issues
However, it faces several threats in the wild, including habitat loss, overcollection, and climate change.
Habitat Loss
Devil’s Tongue Barrel is at risk from habitat loss. With the growth and expansion of human populations, cacti’s natural habitat is being converted into farmland, housing developments, and roads.
A loss of habitat not only causes the cactus to lose its home, but also isolates him, putting him at a greater risk of other types of danger.
Overcollection
There is a serious threat to wild populations of Ferocactus-latispinus due to overcollection among collectors.
The delicate balance of the ecosystem is disrupted when collectors pull the cacti out of the wild. The overcollection of cactus species can cause local extinctions.
Climate Change
This plant is also at risk from climate change. Changing rainfall patterns and temperatures make the habitat less conducive to the cactus’ survival.
It is also possible for cactus populations to be damaged or destroyed by droughts and extreme weather events.
Conservation Efforts
Devil’s Tongue Barrel is being protected in several ways. Among these efforts are:
- Protecting the habitat of the cactus by creating protected areas.
- Rather than collecting cacti from the wild, collectors should gather them from nurseries.
- Wild populations can be supplemented by captive breeding of the cactus.
Toxicity of Ferocactus-latispinus
Toxicity to Humans
It is characterized by its sharp spines as well as its saponin substance, a natural chemical that can irritate the skin and cause discomfort.
Redness, itching, and burning can result from contact with the spines. A severe reaction may result in blistering and allergic reactions.
There is also the possibility of harm from ingesting any part of the Ferocactus-latispinus plant.
In addition to causing nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, alkaloids in the plant can trigger gastrointestinal distress. Seizures and respiratory depression may develop in extreme cases.
Toxicity to Cats and Dogs
This plant is toxic to cats and dogs as well as humans. Vomiting, diarrhea, and lethargy can occur after ingesting any part of the plant.
Internal injuries and puncture wounds can be caused if the spines are ingested.
Prevention is Key
It is essential to keep Devil’s Tongue Barrel away from humans and pets in order to prevent harm. Store it away from children and animals so that they cannot easily access it.
Protect your hands from the spines of the cactus by wearing gloves. Take your child or pet to the hospital immediately if you suspect they have eaten parts of the plant.
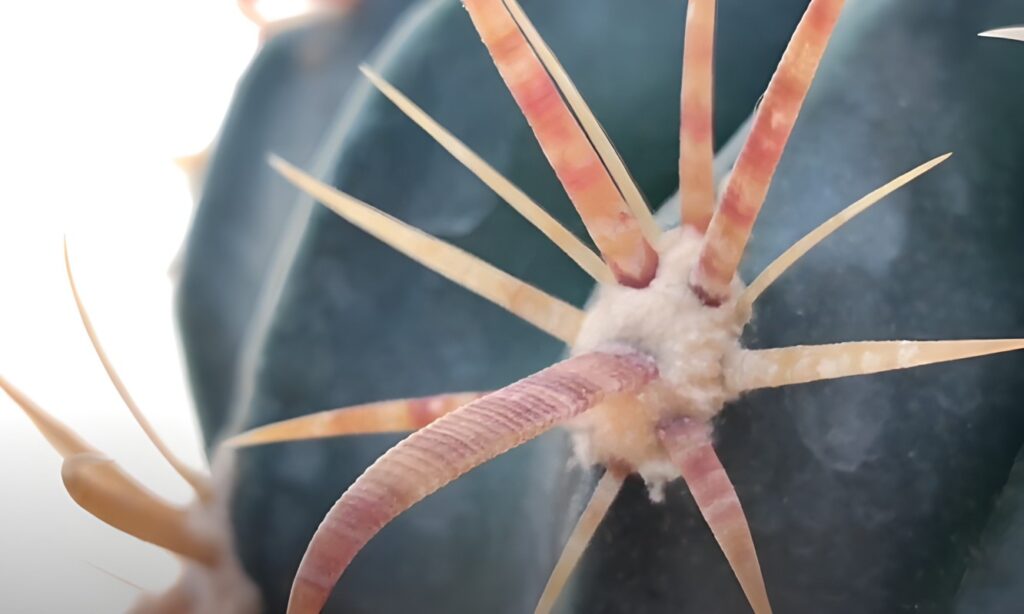

Suggested Uses
Ornamental Delight: Its barrel shape and vibrant blooms make Ferocactus-latispinus a charming addition to any garden. Container-friendly, it can be used indoors, on patios, and on balconies.
Culinary Treat: Devil’s Tongue Barrel trees produce young fruits with a sweet, tangy flavor reminiscent of watermelon. They can be eaten as snacks or added to jams, preserves, and confections to create an original flavor.
Livestock Forage: Animals grazing in arid regions benefit greatly from your this plant. Animals are able to survive during dry periods due to its fleshy stems, which provide moisture and nutrients.
Traditional Medicine Traditionally, Ferocactus plant extracts have been used to treat inflammation, bacteria, and antioxidants. Natural remedies could be found here.
Erosion Control: Arid regions are protected from erosion by Ferocactus-latispinus’ robust roots. As a result of its presence, ecosystems are more stable, contributing to their resilience.
Pollinator Haven: In addition to bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds, vibrant blooms attract pollinators. Desert flora rely on it for reproductive success, which supports biodiversity.
Educational Tool: A desert flora educational tool, Ferocactus-latispinus demonstrates unique adaptations to desert life, including the ability to store water and defend itself from predators.
Conservation Icon: A desert plant, Devil’s Tongue Barrel symbolizes resilience since it thrives in harsh environments and contributes to the delicate balance of desert ecosystems.
Top Tips for Optimal Growth
Apot with adequate drainage holes is best for Ferocactus-latispinus to avoid waterlogging. In addition to allowing the soil to breathe, terracotta pots allow it to dry out very quickly.
This plant can thrives when it receives plenty of direct sunlight, so make sure it receives at least 6 hours of direct sunlight every day. The hottest part of the day may require some shade if you live in a hot climate
The Ferocactus-latispinus plant does not require frequent watering since it is drought-tolerant. Between waterings, allow the soil to completely dry out. Watering may only be needed once a month or less during the winter months.
It is more likely to thrive in a well-draining cacti and succulent soil mix. As a result, root rot will be prevented.
To accommodate the larger root system of Devil’s Tongue Barrel, repotte it every few years as it grows. The new pot should only be slightly larger than the old one.
Fertilize Occasionally: Feed Ferocactus-latispinus with diluted cactus fertilizer during the spring and summer months. The plant is dormant during the winter months, so it should not be fertilized.
You should protect your Ferocactus plant from frost if you live in a cold climate. Plants should be brought indoors or wrapped in frost blankets during the winter.
Exploring the Market
Availability for Purchase
In addition to online retailers and nurseries, specialty cactus shops are widely available for purchasing Ferocactus latispinus, also known as Devil’s Tongue Barrel Cactus. Small seedlings through mature specimens are available for purchase.
Price Ranges
Size, maturity, and variety of Ferocactus latispinus determine the price. A seedling typically costs around $10, while a large mature specimen can cost from $50 to $200.
Popular Varieties
Ferocactus latispinus is available in several varieties, each with its own characteristics. The following varieties are among the most sought-after:
- Ferocactus latispinus ‘Aureus’: Gold-yellow spines distinguish this variety.
- Ferocactus latispinus ‘Cristata’: The unique growth form of this variety makes it a striking ornamental plant.
- Ferocactus latispinus ‘Glochidiatus’: The glochids of this variety resemble fine hairs.
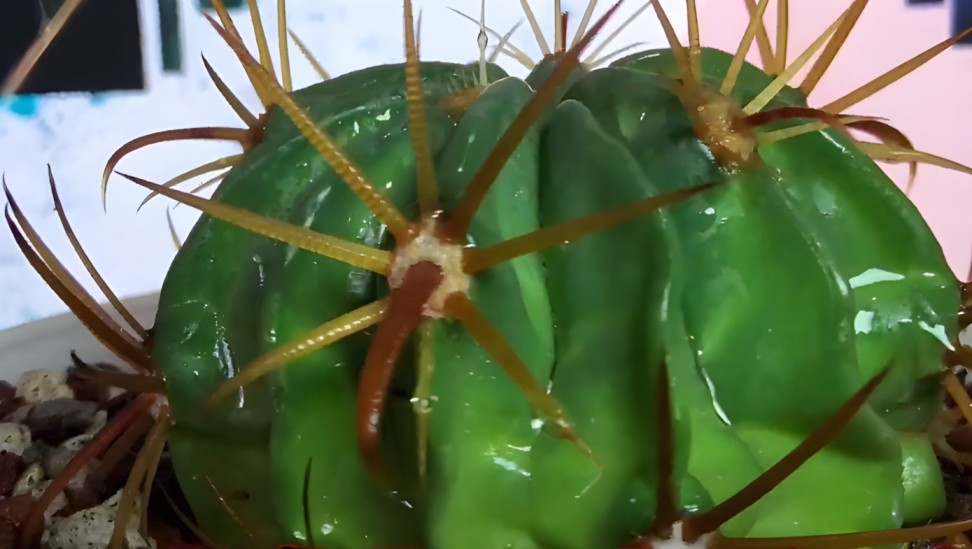

Varieties and Types
Ferocactus latispinus exhibits several fascinating varieties, each with its unique characteristics:
- Ferocactus latispinus var. latispinus: With broad, flattened spines and orange or yellow flowers, this is the most common variety.
- Ferocactus latispinus var. Greenwoodii: Characterized by its nearly straight central spines and ball-shaped stems.
- Ferocactus latispinus var. A spiraled or twisted spine gives this species its distinctive appearance.
Ferocactus latispinus exhibits remarkable adaptability with every variety, adding a touch of diversity to its species.
Comprehensive Care Guide for Ferocactus latispinus and Diverse Cactus Varieties
Caring for a Ferocactus latispinus requires attention to various aspects, from its unique devil’s tongue appearance to its specific care needs. The purchase (achat) of this cactus, known for its stunning blüte (blooms) and striking yellow spines, might entail considerations beyond typical cactus care.
The cuidados (care) for Ferocactus latispinus involve understanding its disease-resistant nature and implementing proper entretien (maintenance) practices. When looking for Ferocactus latispinus for sale, it’s essential to assess the plant’s overall health, growth rate, and potential floral display.
The plant’s hauteur (height) and visual appeal in a jardin (garden) or indoor space can be enhanced with suitable care. For specific issues like maladie (disease) or concerns about roots and spiralis growth, referring to expert resources such as LLIFLE or jardin images is advisable.
Whether dealing with a nain (dwarf) variety or considering when to planter (plant), the Ferocactus latispinus, with its varied cultivars like var. flavispinus and var. flavipinnis, offers a rich palette for succulent enthusiasts.
Additionally, understanding general cactus care principles, such as those applicable to ferocactus recurvus or cylindraceus, is crucial. For those delving into the broader world of cacti, recognizing the distinct features of coloratus and other ferocactus types is essential.
Exploring how to feed and fertilize cacti, including zygocactus, contributes to overall plant health. Specific concerns like pee turning bright yellow due to vitamins or addressing a golden barrel cactus turning yellow require attentive care.
Whether it’s fero care syrup or considerations for gasteria growth, the vast array of cactus varieties, each with its unique characteristics, adds a delightful challenge to cultivating these resilient and captivating plants.
Conclusion
A captivating species native to Mexico, Ferocactus latispinus, also known as Devil’s Tongue Barrel or Candy Cactus, is celebrated for its spines, colorful blooms, and unique features.
The plant has a wide range of uses, including ornamental delight and culinary delight as well as livestock forage, traditional medicine, erosion control, and pollinator habitat. Conservation efforts are crucial due to threats such as habitat loss and overcollection in the wild.
There is a potential for toxicity despite its beauty. You should provide your plants with plenty of sunlight, water them sparingly, and use soil that drains well. Variety adds diversity to this resilient cactus species, which is available at varying price points.
FAQs
What is the name of Ferocactus latispinus?
Devil’s tongue cactus, Candy cactus, Crow’s Claw Cactus
What is the fruit of the devil’s tongue cactus?
Known for its deep red fruits, Ferocactus latispinus has large, edible fruits. In addition to having a sweet and tangy flavor, the fruits are about 2.5 cm (1 inch) in diameter and have a juicy flesh.
What is the common name of Ferocactus?
The Common name of Ferocactus is Barrel cactus.
What is the common name for Ferocactus viridescens?
The common name for Ferocactus viridescens is Green barrel cactus
What is the most beautiful Ferocactus? How long does Ferocactus live?
Chin cactus is the most beautiful Ferocactus. Ferocactus cacti can live for many years, with some specimens reaching over 100 years old.
What are the health benefits of Ferocactus?
Ferocactus cacti are said to have a number of health benefits, including:
- Reducing stress and anxiety
- Improving air quality
- Boosting energy levels
- Promoting relaxation
Does Ferocactus flower? At what age do ferocactus flower?
The Ferocactus cactus flowers in late autumn or early winter, depending on the region. Colors include purple, yellow, and red for the funnel-shaped flowers. Depending on the species and growing conditions, ferocactus cacti can start flowering as soon as 5 years old.
What is the largest Ferocactus?Are Ferocactus edible?
The Ferocactus latispinus cactus is edible and is one of the Ferocactus species. Vitamins and minerals are plentiful in these fruits, which can be eaten fresh, cooked, or made into jam or jelly.
What is the location of Ferocactus?
Mexican and southwestern U.S. cacti are known as ferocactus cacti. Dry, desert regions are usually where they can be found.
How do I identify a Ferocactus?
The globular, spine-covered bodies of Ferocactus cacti are characterized by their globular or barrel-shaped shape. Numerous ribs can be found on them, which may be straight or curved.
In addition to long and flat spines, needle-like spines can also be found. Flower colors can range from purple to yellow to red on Ferocactus cacti.
How do you care for a Ferocactus latispinus?
There is little difficulty in caring for Ferocactus latispinus cacti. It is important to use a potting mix that drains well and provide plenty of sunlight to these plants.
The soil should be allowed to dry out completely between waterings, and they should be watered deeply but infrequently. Heat and drought are not problems for Ferocactus latispinus, but frost can be a problem.
What is the history of the Ferocactus?
It was not until the early 1800s that ferocactus cacti were described. Its edible fruits and ornamental value have made them a popular crop for centuries. Food and shelter are provided by ferocactus cacti in the desert ecosystem.
How big does a devil’s tongue cactus get?
The Devil’s tongue cactus grows to a height of 6 feet and a width of 3 feet.
How do you propagate the devil’s tongue cactus?
Seeds and offsets are two ways of propagating Devil’s tongue cacti. Keeping seeds moist and warm is important when propagating from seeds.
Offsets can be propagated by removing them from the parent plant and letting them callus over for a few days before planting them in a well-draining medium.






